Prerequisites
To follow the steps on this page:- Create a target with the Real-time analytics capability enabled. You need your connection details. This procedure also works for .
- Install self-managed Grafana or sign up for Grafana Cloud.
Connect Grafana to Tiger Cloud
To visualize the results of your queries, enable Grafana to read the data in your :-
Log in to Grafana
In your browser, log in to either:
- Self-hosted Grafana: at
http://localhost:3000/. The default credentials areadmin,admin. - Grafana Cloud: use the URL and credentials you set when you created your account.
- Self-hosted Grafana: at
-
Add your as a data source
-
Open
Connections>Data sources, then clickAdd new data source. -
Select
PostgreSQLfrom the list. -
Configure the connection:
-
Host URL,Database name,Username, andPasswordConfigure using your connection details.Host URLis in the format<host>:<port>. -
TLS/SSL Mode: selectrequire. -
PostgreSQL options: enableTimescaleDB. - Leave the default setting for all other fields.
-
-
Click
Save & test.
-
Open
Create a Grafana dashboard and panel
Grafana is organized into dashboards and panels. A dashboard represents a view into the performance of a system, and each dashboard consists of one or more panels, which represent information about a specific metric related to that system. To create a new dashboard:-
On the
Dashboardspage, clickNewand selectNew dashboard -
Click
Add visualization - Select the data source Select your from the list of pre-configured data sources or configure a new one.
- Configure your panel Select the visualization type. The type defines specific fields to configure in addition to standard ones, such as the panel name.
-
Run your queries
You can edit the queries directly or use the built-in query editor. If you are visualizing time-series data, select
Time seriesin theFormatdrop-down. -
Click
Save dashboardYou now have a dashboard with one panel. Add more panels to a dashboard by clickingAddat the top right and selectingVisualizationfrom the drop-down.
Use the time filter function
Grafana time-series panels include a time filter:-
Call
$__timefilter()to link the user interface construct in a Grafana panel with the query For example, to set thepickup_datetimecolumn as the filtering range for your visualizations: -
Group your visualizations and order the results by time buckets
In this case, the
GROUP BYandORDER BYstatements referencetime. For example:When you visualize this query in Grafana, you see this: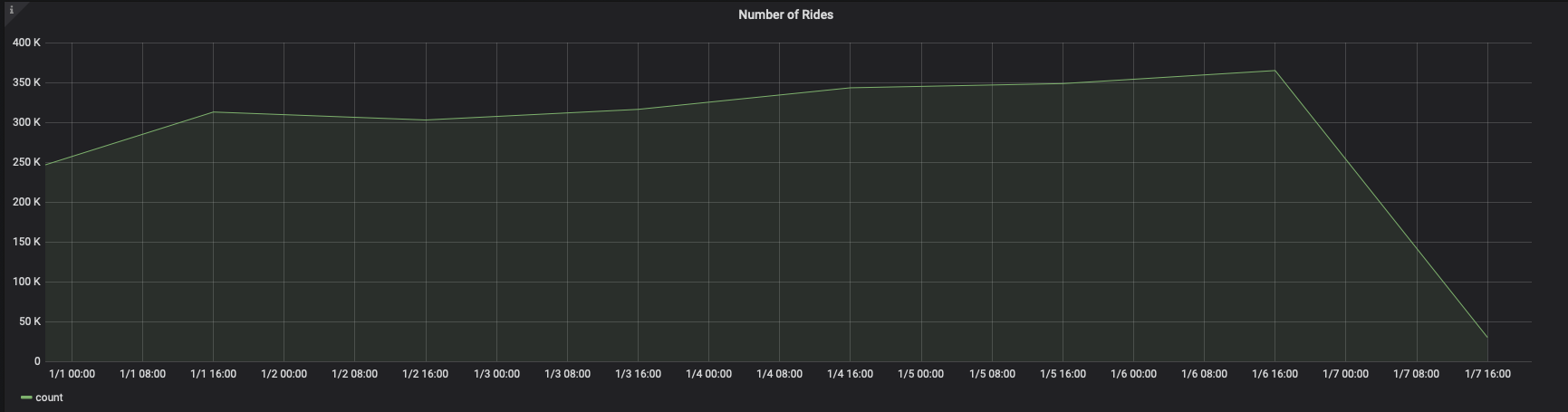 You can adjust the
You can adjust the time_bucketfunction and compare the graphs:When you visualize this query, it looks like this: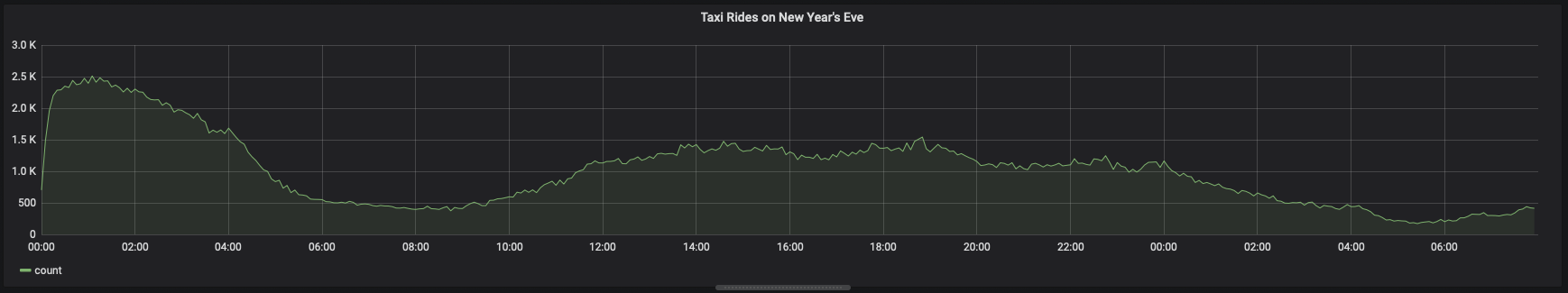
Visualize geospatial data
Grafana includes a Geomap panel so you can see geospatial data overlaid on a map. This can be helpful to understand how data changes based on its location. This section visualizes taxi rides in Manhattan, where the distance traveled was greater than 5 miles. It uses the same query as the NYC Taxi Cab tutorial as a starting point.-
Add a geospatial visualization
-
In your Grafana dashboard, click
Add>Visualization. -
Select
Geomapin the visualization type drop-down at the top right.
-
In your Grafana dashboard, click
-
Configure the data format
-
In the
Queriestab below, select your data source. -
In the
Formatdrop-down, selectTable. -
In the mode switcher, toggle
Codeand enter the query, then clickRun. For example:
-
In the
-
Customize the Geomap settings
With default settings, the visualization uses green circles of the fixed size. Configure at least the following for a more representative view:
-
Map layers>Styles>Size>value. This changes the size of the circle depending on the value, with bigger circles representing bigger values. -
Map layers>Styles>Color>value. -
Thresholds> Addthreshold. Add thresholds for 7 and 10, to mark rides over 7 and 10 miles in different colors, respectively.

-

