 The leverages the well-established logical replication protocol. By relying on this protocol,
it ensures compatibility, familiarity, and a broader knowledge base—making it easier for you to adopt the connector
and integrate your data.
You use the for data synchronization, rather than migration. This includes:
The leverages the well-established logical replication protocol. By relying on this protocol,
it ensures compatibility, familiarity, and a broader knowledge base—making it easier for you to adopt the connector
and integrate your data.
You use the for data synchronization, rather than migration. This includes:
-
Copy existing data from a instance:
- Copy data at up to 150 GB/hr. You need at least a 4 CPU/16 GB source database, and a 4 CPU/16 GB target .
- Copy the publication tables in parallel. Large tables are still copied using a single connection. Parallel copying is in the backlog.
-
Forget foreign key relationships.
The connector disables foreign key validation during the sync. For example, if a
metricstable refers to theidcolumn on thetagstable, you can still sync only themetricstable without worrying about their foreign key relationships. -
Track progress.
exposes
COPYprogress underpg_stat_progress_copy.
- Synchronize real-time changes from a instance.
- Add and remove tables on demand using the PUBLICATION interface.
- Enable features such as s, , and s on your logical replica.
- Tiger Console
- Self-hosted Postgres connector
Prerequisites
To follow the steps on this page:- Create a target with real-time analytics enabled. You need your connection details.
- Install the client tools on your sync machine.
- Ensure that the source instance and the target have the same extensions installed. The does not create extensions on the target. If the table uses column types from an extension, first create the extension on the target before syncing the table.
Limitations
- The source instance must be accessible from the Internet. Services hosted behind a firewall or VPC are not supported. This functionality is on the roadmap.
- Indexes, including the primary key and unique constraints, are not migrated to the target. We recommend that, depending on your query patterns, you create only the necessary indexes on the target.
- This works for databases only as source. is not yet supported.
- The source must be running 13 or later.
- Schema changes must be co-ordinated. Make compatible changes to the schema in your first, then make the same changes to the source instance.
- Ensure that the source instance and the target have the same extensions installed. The does not create extensions on the target. If the table uses column types from an extension, first create the extension on the target before syncing the table.
- There is WAL volume growth on the source instance during large table copy.
-
Continuous aggregate invalidation
The connector uses
session_replication_role=replicaduring data replication, which prevents table triggers from firing. This includes the internal triggers that mark continuous aggregates as invalid when underlying data changes. If you have continuous aggregates on your target database, they do not automatically refresh for data inserted during the migration. This limitation only applies to data below the continuous aggregate’s materialization watermark. For example, backfilled data. New rows synced above the continuous aggregate watermark are used correctly when refreshing. This can lead to:- Missing data in continuous aggregates for the migration period.
- Stale aggregate data.
- Queries returning incomplete results.
forceoption ofrefresh_continuous_aggregate.
Set your connection string
This variable holds the connection information for the source database. In the terminal on your migration machine, set the following:Tune your source database
- From AWS RDS/Aurora
- From Postgres
Updating parameters on a instance will cause an outage. Choose a time that will cause the least issues to tune this database.
-
Tune the Write Ahead Log (WAL) on the RDS/Aurora source database
- In https://console.aws.amazon.com/rds/home#databases:, select the RDS instance to migrate.
-
Click
Configuration, scroll down and note theDB instance parameter group, then clickParameter Groups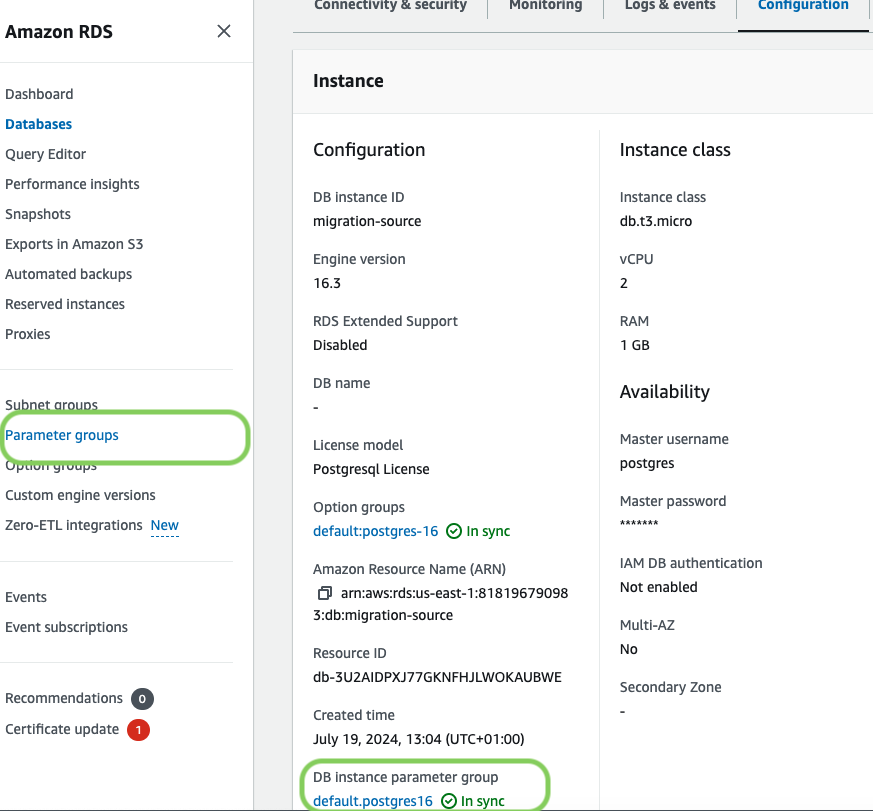
-
Click
Create parameter group, fill in the form with the following values, then clickCreate.- Parameter group name - whatever suits your fancy.
- Description - knock yourself out with this one.
- Engine type -
PostgreSQL - Parameter group family - the same as
DB instance parameter groupin yourConfiguration.
-
In
Parameter groups, select the parameter group you created, then clickEdit. -
Update the following parameters, then click
Save changes.rds.logical_replicationset to1: record the information needed for logical decoding.wal_sender_timeoutset to0: disable the timeout for the sender process.
-
In RDS, navigate back to your databases, select the RDS instance to migrate, and click
Modify. -
Scroll down to
Database options, select your new parameter group, and clickContinue. -
Click
Apply immediatelyor choose a maintenance window, then clickModify DB instance. Changing parameters will cause an outage. Wait for the database instance to reboot before continuing. - Verify that the settings are live in your database.
-
Create a user for the and assign permissions
-
Create
<pg connector username>:You can use an existing user. However, you must ensure that the user has the following permissions. -
Grant permissions to create a replication slot:
-
Grant permissions to create a publication:
-
Assign the user permissions on the source database:
If the tables you are syncing are not in the
publicschema, grant the user permissions for each schema you are syncing: -
On each table you want to sync, make
<pg connector username>the owner:You can skip this step if the replicating user is already the owner of the tables.
-
Create
-
Enable replication
DELETEandUPDATEoperations Replica identity assists data replication by identifying the rows being modified. Your options are that each table and hypertable in the source database should either have:- A primary key: data replication defaults to the primary key of the table being replicated. Nothing to do.
-
A viable unique index: each table has a unique, non-partial, non-deferrable index that includes only columns
marked as
NOT NULL. If a UNIQUE index does not exist, create one to assist the migration. You can delete if after migration. For each table, setREPLICA IDENTITYto the viable unique index: -
No primary key or viable unique index: use brute force.
For each table, set
REPLICA IDENTITYtoFULL:For eachUPDATEorDELETEstatement, reads the whole table to find all matching rows. This results in significantly slower replication. If you are expecting a large number ofUPDATEorDELETEoperations on the table, best practice is to not useFULL.
Synchronize data to your Tiger Cloud service
To sync data from your database using :- Connect to your In , select the to sync live data to.
-
Connect the source database and the target
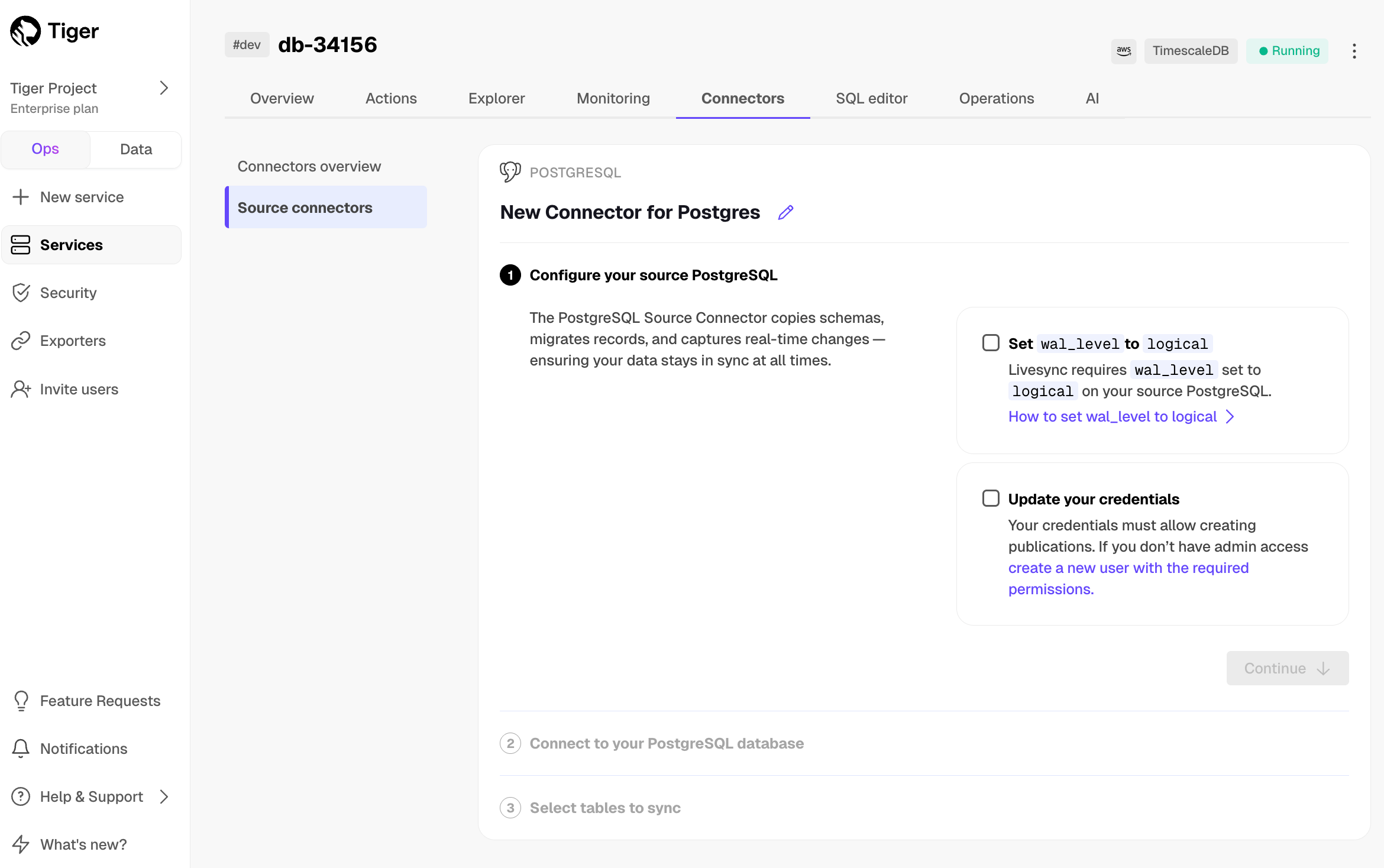
- Click
Connectors>PostgreSQL. - Set the name for the new connector by clicking the pencil icon.
- Check the boxes for
Set wal_level to logicalandUpdate your credentials, then clickContinue. - Enter your database credentials or a connection string, then click
Connect to database. This is the connection string for<pg connector username>. The console connects to the source database and retrieves the schema information.
- Click
-
Optimize the data to synchronize in hypertables
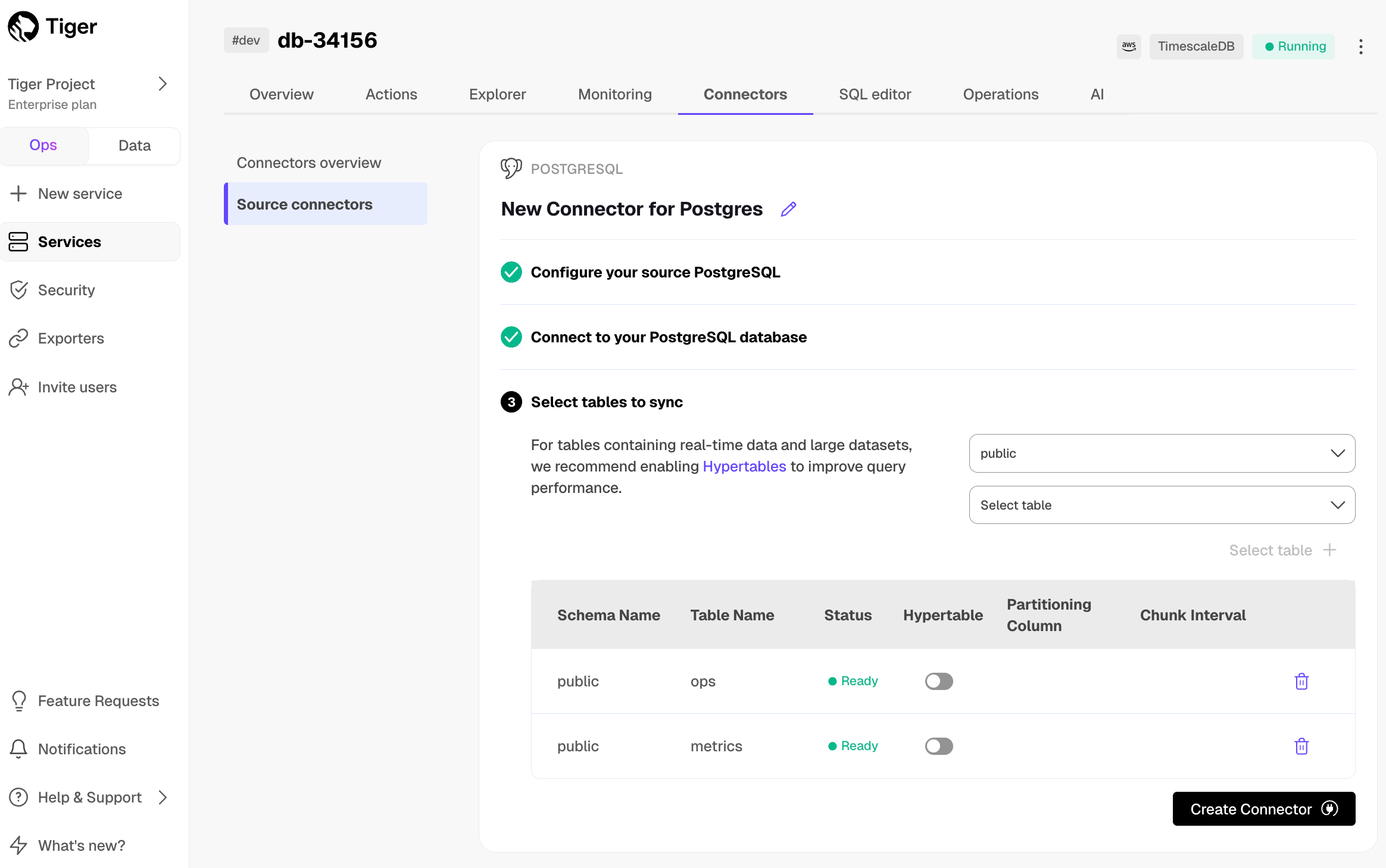
-
In the
Select tabledropdown, select the tables to sync. -
Click
Select tables +. The console checks the table schema and, if possible, suggests the column to use as the time dimension in a . -
Click
Create Connector. The console starts the connector between the source database and the target and displays the progress.
-
In the
-
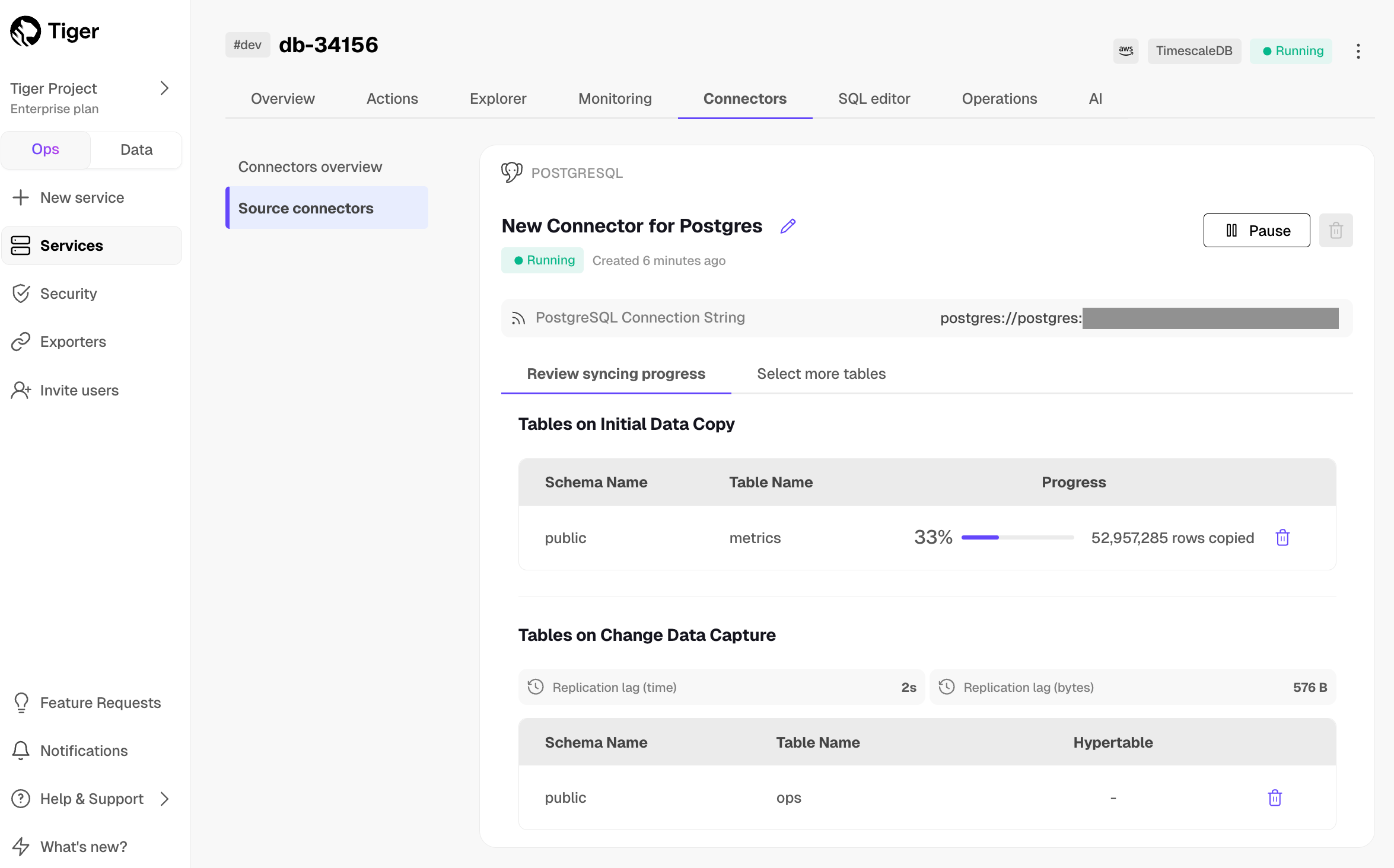
Monitor synchronization

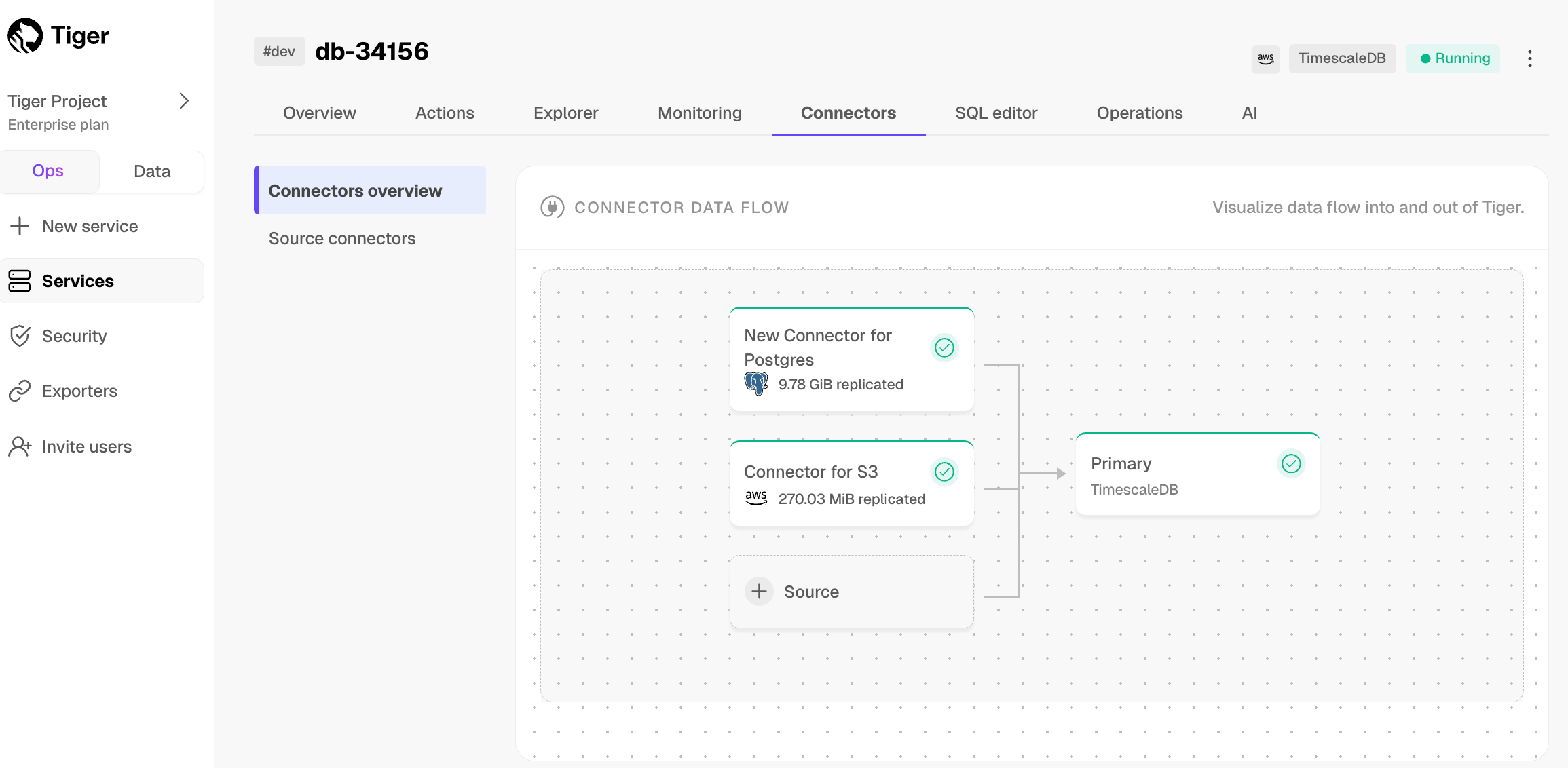
-
To view the amount of data replicated, click
Connectors. The diagram inConnector data flowgives you an overview of the connectors you have created, their status, and how much data has been replicated. -
To review the syncing progress for each table, click
Connectors>Source connectors, then select the name of your connector in the table.
-
To view the amount of data replicated, click
-
Manage the connector
-
To edit the connector, click
Connectors>Source connectors, then select the name of your connector in the table. You can rename the connector, delete or add new tables for syncing. -
To pause a connector, click
Connectors>Source connectors, then open the three-dot menu on the right and selectPause. -
To delete a connector, click
Connectors>Source connectors, then open the three-dot menu on the right and selectDelete. You must pause the connector before deleting it.
-
To edit the connector, click

